How to operate a drone? This seemingly simple question opens a world of possibilities, from capturing breathtaking aerial photography to exploring the intricacies of advanced flight maneuvers. This guide provides a structured approach to mastering drone operation, covering everything from pre-flight checks and safety protocols to advanced techniques and troubleshooting common issues. Whether you’re a novice pilot or seeking to refine your skills, this comprehensive resource will empower you to confidently navigate the skies.
We will delve into the essential aspects of drone piloting, ensuring you understand not only the technical controls but also the crucial safety regulations and best practices for responsible drone operation. From understanding your drone’s controls and flight modes to mastering camera settings and battery management, this guide is your key to unlocking the full potential of your drone.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight checklist is crucial for ensuring safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting the drone’s components, understanding and adhering to local regulations, and establishing a safe takeoff and landing procedure. Neglecting these steps can lead to accidents and damage.
Drone Pre-Flight Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection helps identify potential issues before they cause problems during flight. The following checklist should be performed meticulously before each flight:
| Component | Check | Pass/Fail | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Inspect for damage, cracks, or imbalance. | Replace damaged propellers immediately. | |
| Motors | Visually inspect for damage and ensure they spin freely. | Listen for unusual noises during a brief motor test. | |
| Battery | Check battery level and ensure it’s properly connected. | Use only manufacturer-approved batteries. | |
| Camera | Confirm camera is securely mounted and functioning correctly. | Test camera functionality before takeoff. | |
| Gimbal (if applicable) | Check gimbal movement and ensure it’s properly calibrated. | Recalibrate if necessary. | |
| GPS Signal | Ensure a strong GPS signal is acquired before takeoff. | Sufficient satellites are needed for stable flight. | |
| Remote Controller | Check battery level and ensure proper connection to the drone. | Test all controls before takeoff. | |
| Airframe | Inspect for any damage or loose parts. | Pay attention to any cracks or bending of the frame. |
Understanding and Adhering to Regulations
Operating a drone requires awareness and strict adherence to local regulations and airspace restrictions. These regulations vary by country and region, often specifying permitted flight altitudes, locations, and operational limitations. Failure to comply can result in fines or legal consequences.
Safe Takeoff and Landing Procedures
Safe takeoff and landing procedures are crucial for preventing accidents. A smooth, controlled takeoff and landing minimizes the risk of damage to the drone or surrounding environment. Emergency protocols should be practiced and understood to handle unexpected situations.
- Perform a pre-flight check.
- Select a clear, open area away from obstacles and people.
- Slowly raise the drone to a safe height.
- Maintain visual contact with the drone at all times.
- For landing, slowly descend the drone to the ground.
- In case of emergency, immediately engage the emergency stop feature (if available) or bring the drone down safely in a controlled manner.
Drone Controls and Navigation: How To Operate A Drone
Understanding your drone’s controls and navigation systems is essential for safe and efficient operation. This section covers the basic functions of the transmitter, various flight modes, and navigating to specific locations using GPS coordinates.
Drone Transmitter Controls
Most drone transmitters utilize two joysticks for controlling the drone’s movement and buttons/dials for additional functions. The left joystick typically controls altitude and yaw (rotation), while the right joystick controls direction and pitch/roll (tilting). Buttons are used for features such as camera control, return-to-home, and emergency stops.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability. GPS mode utilizes satellite signals for position holding and autonomous flight, offering greater stability. Attitude mode maintains the drone’s orientation regardless of GPS signal, useful in GPS-denied environments. Manual mode provides complete control, ideal for experienced pilots but requiring more skill.
Navigating to a Specific Location
Navigating a drone to a specific location using GPS coordinates involves inputting the coordinates into the drone’s flight controller and initiating a waypoint navigation function. This often requires using the drone’s app or software.
Flowchart Description: The flowchart begins with “Input GPS Coordinates.” This leads to “Drone Receives Coordinates” which branches to “GPS Signal Strong?” Yes leads to “Initiate Navigation,” No leads to “Wait for GPS Signal.” “Initiate Navigation” leads to “Drone Navigates to Coordinates,” then “Reached Destination?” Yes ends the flowchart, No loops back to “Drone Navigates to Coordinates.”
Camera Operation and Image Capture
The drone’s camera is a key feature, allowing for capturing stunning aerial photography and videography. Understanding camera settings and recording techniques is crucial for achieving optimal image and video quality.
Adjusting Camera Settings

Adjusting camera settings such as ISO, shutter speed, and aperture is essential for achieving optimal image quality in various lighting conditions. Higher ISO values are suitable for low-light conditions, but they can introduce noise. Shutter speed affects motion blur, while aperture controls depth of field.
Recording High-Quality Video
Recording high-quality video involves selecting the appropriate video resolution, frame rate, and bitrate. Higher resolutions and frame rates result in smoother, more detailed videos, but they require more storage space. Bitrate affects the video’s compression and quality.
Key Camera Parameters

| Setting | Description | Impact on Image/Video | Recommended Value (Example) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO | Sensitivity to light | Higher ISO increases brightness but introduces noise | 100-400 |
| Shutter Speed | Duration the sensor is exposed to light | Faster shutter speed reduces motion blur, slower increases it | 1/125s – 1/500s |
| Aperture | Size of the lens opening | Controls depth of field and light intake | f/2.8 – f/5.6 |
| Resolution | Image size in pixels | Higher resolution produces larger, more detailed images/videos | 4K |
| Frame Rate | Frames per second | Higher frame rates create smoother videos | 24-60 fps |
| Bitrate | Data rate of video | Higher bitrate improves video quality but increases file size | 50-100 Mbps |
Battery Management and Flight Time
Proper battery management is crucial for maximizing flight time and extending the lifespan of your drone batteries. Understanding factors affecting flight time and estimating remaining flight time are essential for safe operation.
Understanding drone operation involves several key aspects, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning to safely and effectively pilot a drone requires practice and understanding of regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all these aspects, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone to build your skills and confidence. Ultimately, responsible drone operation ensures both safety and enjoyable flight experiences.
Charging and Storing Batteries
Always use the manufacturer-recommended charger and follow the charging instructions carefully. Avoid overcharging or discharging batteries completely. Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight or extreme temperatures.
Factors Affecting Flight Time
Several factors affect flight time, including wind conditions, payload (camera, accessories), and flight mode. Strong winds increase energy consumption, while heavier payloads reduce flight time. Aggressive flight modes also consume more power.
Estimating Remaining Flight Time, How to operate a drone
Estimating remaining flight time can be done by monitoring the battery level indicator and calculating the consumption rate. For example, if the battery is at 50% and the average consumption rate is 20% per 10 minutes, the remaining flight time is approximately 25 minutes (50%/20%
– 10 minutes).
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Familiarizing yourself with common drone malfunctions and their troubleshooting steps is essential for handling issues effectively. This section covers common problems and their potential solutions.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Troubleshooting
Several common issues can occur during drone operation. Quick identification and appropriate troubleshooting steps are crucial for resolving these issues and preventing further damage.
- GPS Signal Loss:
- Check for obstructions blocking the GPS signal.
- Ensure sufficient satellites are acquired.
- Relocate to an area with better GPS reception.
- Low Battery Warning:
- Land the drone immediately.
- Check the battery level and charge as needed.
- Avoid pushing the battery to its limits.
- Motor Failure:
- Inspect motors for damage.
- Check motor connections.
- Replace faulty motors.
- Gimbal Malfunction:
- Check gimbal calibration.
- Inspect gimbal for damage or obstructions.
- Restart the drone.
- Remote Controller Issues:
- Check remote controller battery level.
- Ensure proper connection between the remote and drone.
- Restart both the remote and drone.
Drone Maintenance and Cleaning
Regular maintenance and cleaning are essential for ensuring the optimal performance and longevity of your drone. This involves cleaning the drone’s components and performing routine checks to identify potential issues.
Cleaning and Maintenance
Clean the drone’s body, propellers, and camera lens regularly using a soft cloth and appropriate cleaning solution. Inspect all components for wear and tear, and replace damaged parts as needed. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for cleaning and maintenance.
Drone Component Locations
Detailed Description (no image): The drone’s main body typically houses the flight controller, battery compartment, and camera. The propellers are attached to the motors, located at each corner of the body. The gimbal (if present) is mounted below the camera. Antennas are usually located on top or sides of the body. The landing gear is located at the bottom of the drone.
Advanced Flight Techniques
Mastering advanced flight techniques enhances your drone piloting skills and opens up creative possibilities for aerial photography and videography. This section covers basic and advanced maneuvers and discusses different flight controllers.
Basic Aerial Maneuvers
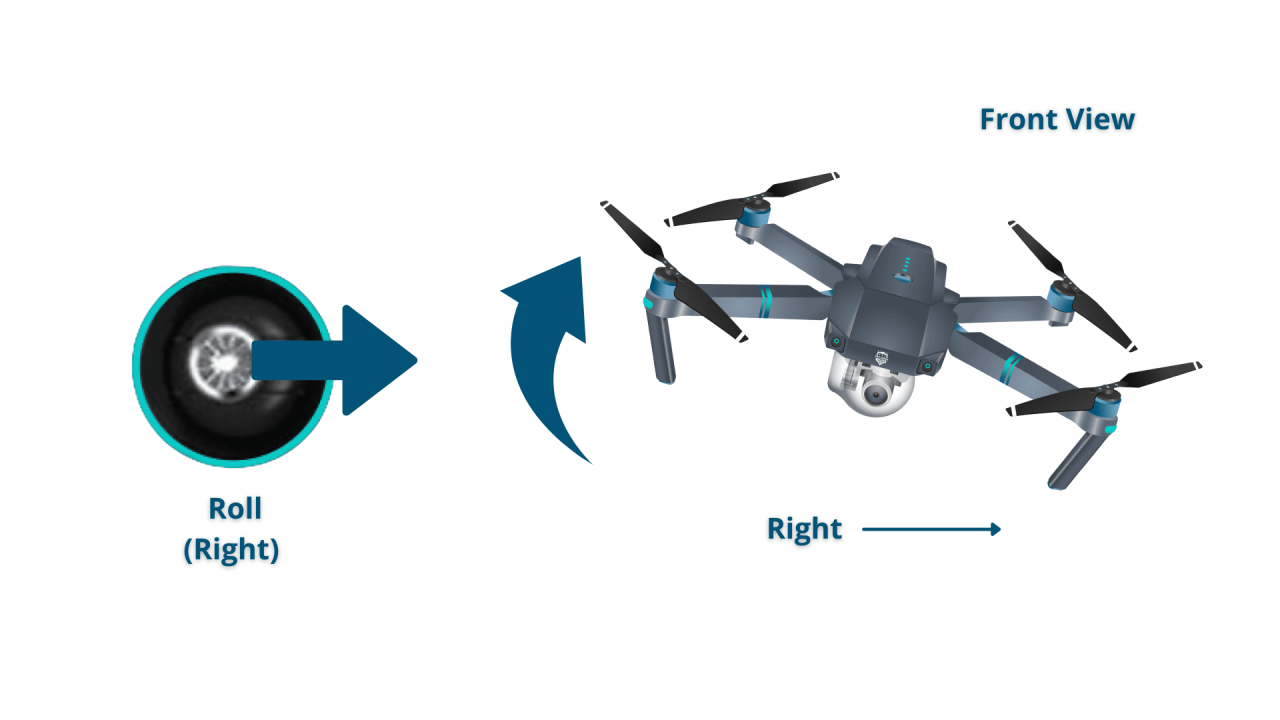
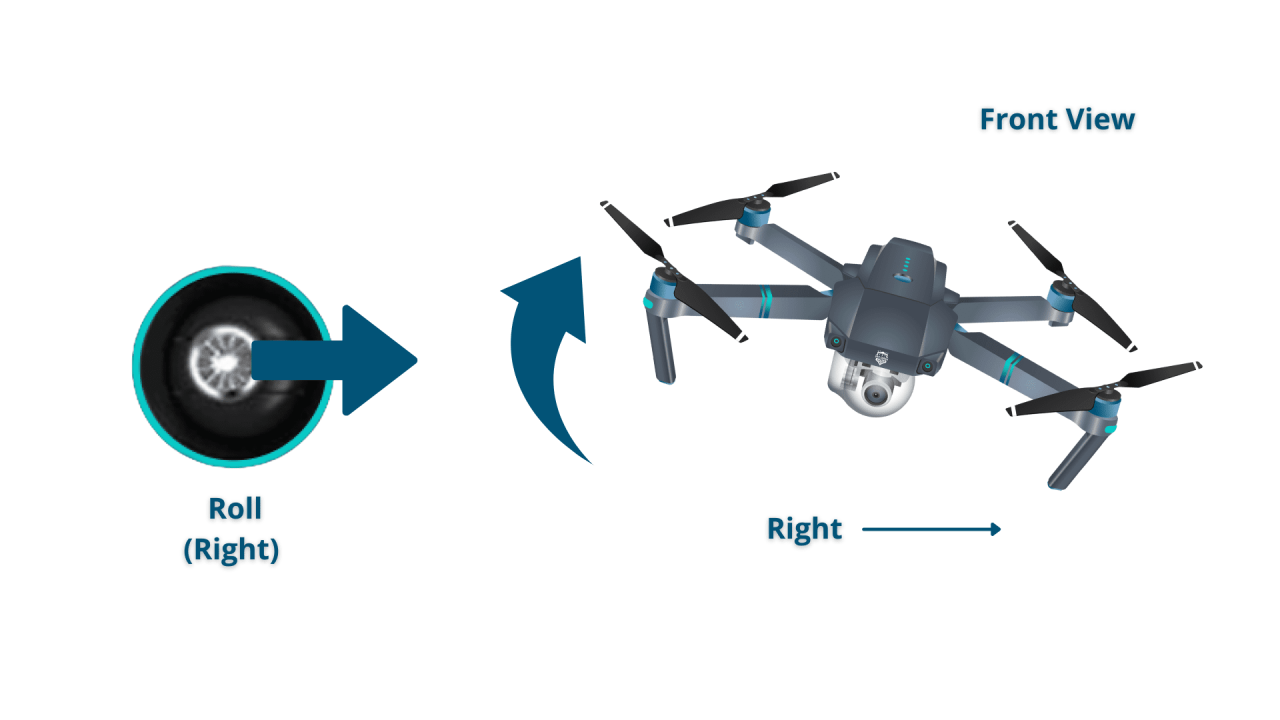
Basic maneuvers include hovering (maintaining a fixed position), yaw (rotating around the vertical axis), pitch (tilting forward or backward), and roll (tilting left or right). Practicing these maneuvers is crucial for developing control and stability.
Cinematic Shots
Cinematic shots such as orbit (circling a subject), follow (following a moving subject), and point of interest (keeping a specific point in frame) require precise control and understanding of the drone’s capabilities. Planning and practice are essential for achieving smooth and professional-looking shots.
Flight Controllers
Different flight controllers offer varying levels of maneuverability and stability. Some controllers prioritize stability, while others offer greater responsiveness for acrobatic maneuvers. The choice of flight controller depends on the intended application and pilot experience.
Mastering drone operation is a journey of continuous learning and practice. By diligently following the safety guidelines, understanding your drone’s capabilities, and consistently refining your piloting skills, you can confidently and responsibly explore the exciting world of aerial flight. Remember, safe and responsible operation is paramount; always prioritize safety and adhere to all local regulations. The rewards – stunning visuals, innovative applications, and a newfound perspective – are well worth the effort.
Top FAQs
What is the best type of drone for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones are ideal for beginners, often featuring GPS stabilization and autonomous flight modes. Research models with good reviews and ease-of-use features.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrate your drone’s compass before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or experienced interference.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
If your drone loses GPS signal, immediately switch to a lower flight mode (like attitude mode), carefully maneuver it back to a safe location, and land it.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a solid grasp of the regulations and safe operating procedures. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone to enhance your skills and fly responsibly.
Ultimately, safe and proficient drone operation hinges on consistent practice and adherence to best practices.
How do I get a drone pilot license?
Licensing requirements vary by location. Check your country/region’s aviation authority for specific regulations and licensing information.